Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. This article explores the normal blood sugar levels chart, including glucose ranges for fasting, postprandial (after meals), and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. Understanding these ranges, monitoring techniques, factors influencing blood sugar levels, and healthy management practices can help individuals maintain optimal glucose levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, refers to the concentration of glucose present in the bloodstream. Glucose is the body’s primary source of energy and comes from the foods we eat. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy or storage.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
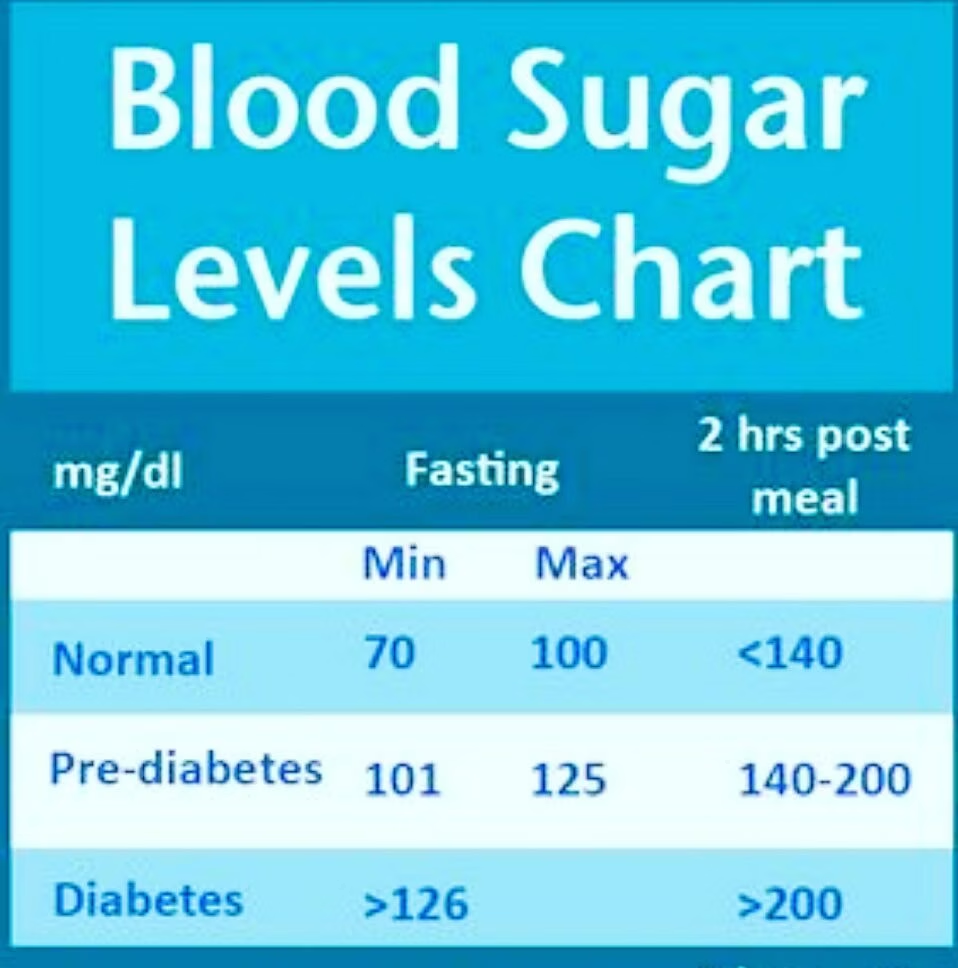
Normal Range: Typically, fasting blood sugar levels should fall between 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Impaired Fasting Glucose (Prediabetes): Fasting blood sugar levels between 100 to 125 mg/dL indicate prediabetes.
Diabetes: Fasting blood sugar levels of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests indicate diabetes.
Postprandial (After Meal) Blood Sugar Levels
Normal Range: Postprandial blood sugar levels should be below 140 mg/dL two hours after a meal.
Diabetes: Postprandial blood sugar levels consistently above 200 mg/dL indicate diabetes.
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Levels
Normal Range: HbA1c levels below 5.7% are considered normal.
Prediabetes: HbA1c levels between 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
Diabetes: HbA1c levels of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicate diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Self-Monitoring Techniques
Blood Glucose Meters: Portable devices that measure blood sugar levels using a small blood sample obtained from a finger prick.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Devices that provide real-time glucose readings through a sensor placed under the skin, offering continuous monitoring and trend analysis.
Regular Testing: Individuals with diabetes or prediabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, following healthcare provider recommendations for timing and frequency.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Various factors can affect blood sugar levels, including:
Diet: Carbohydrate intake, meal timing, and portion sizes influence blood glucose levels.
Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing glucose uptake into muscles.
Stress: Stress hormones can raise blood sugar levels.
Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids or certain antipsychotics, can affect blood glucose levels.
Healthy Management Practices
Lifestyle Modifications
A balanced diet should emphasize the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Keep an eye on your carbohydrate consumption for efficient blood sugar management.
Regular Exercise: Engage in aerobic exercise, strength training, or physical activities to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce insulin resistance and improve blood glucose control.
Stress Reduction: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
Oral Medications: Medications prescribed by healthcare providers to lower blood sugar levels, such as metformin or sulfonylureas.
Insulin Therapy: Insulin injections or insulin pumps for individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes.
Importance of Regular Health Check-ups
Regular visits to healthcare providers are crucial for:
Monitoring Progress: Tracking blood sugar levels, HbA1c, and overall health status.
Adjusting Treatment Plans: Modifying medications, insulin dosages, or lifestyle recommendations based on individual health needs and goals.
Prevention and Early Detection
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels through healthy lifestyle habits, regular monitoring, and timely medical intervention can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes or manage diabetes effectively. Early detection of prediabetes allows for proactive measures to prevent progression to diabetes through diet, exercise, and medication as needed.
FAQs
What are blood sugar levels?
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose (sugar) present in the bloodstream. Glucose is the body’s primary source of energy, derived from the foods we eat, particularly carbohydrates.
How are blood sugar levels measured?
Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood (mg/dL) in most countries, or millimoles per liter (mmol/L) in some regions. A small sample of blood is typically obtained by pricking a finger or using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
What are normal blood sugar levels?
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day and depend on factors such as diet, physical activity, and individual health status. Generally, for adults without diabetes, the following guidelines apply:
Fasting blood sugar (before meals): Typically between 70-100 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L).
Postprandial blood sugar (1-2 hours after meals): Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
Why is it important to maintain normal blood sugar levels?
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for several reasons:
Energy production: Glucose provides energy to cells throughout the body.
Brain function: The brain relies on glucose as its primary source of fuel.
Preventing complications: High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) can lead to complications such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney damage. Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can cause symptoms like confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness.
What factors can influence blood sugar levels?
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including:
Diet: Foods high in carbohydrates can raise blood sugar levels quickly.
Physical activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing glucose uptake into muscles.
Stress: Stress hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some antipsychotics, can affect blood sugar levels.
Illness: Infections and other illnesses can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
How often should blood sugar levels be checked?
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on individual health factors and whether someone has diabetes or prediabetes. People with diabetes may need to check their blood sugar levels multiple times a day, especially if using insulin or adjusting medications.
What is the glycemic index (GI) and how does it affect blood sugar levels?
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after consumption. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, while foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual increase. Choosing foods with a lower GI can help stabilize blood sugar levels over time.
Understanding the normal blood sugar levels chart, including fasting, postprandial, and HbA1c ranges, is essential for managing blood glucose levels effectively and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can achieve optimal blood sugar control and improve overall health and well-being.
To read more, click here